9 3 Activity-based Costing Financial and Managerial Accounting
So, the businesses need to do a cost-benefit analysis before implementing the ABC system of costing. In addition to this, project planning can also be done with the use of an overhead rate. It’s because it’s an estimated rate and can be predicted at the start of the project.
How to calculate the predetermined overhead rate
This means the manufacturing overhead cost would be applied at 220% of the company’s direct labor cost. It’s a simple step where budgeted/estimated cost is divided with the level of activity calculated in the third stage. It’s called predetermined because both of the figures used in the process are budgeted. To calculate their rate, the marketing agency will need to add up all of its estimated overhead costs for the upcoming year. This means that for every dollar of direct labor costs, the business will incur $0.20 in overhead costs. A Predetermined Overhead rate shall be used to calculate an estimate on the projects that are yet to commence for overhead costs.

What Is Job Costing in Accounting?
- The management concern about how to find a predetermined overhead rate for costing.
- This is done by dividing the total estimated overhead costs by the total estimated direct labor hours or machine hours.
- Sales of each product have been strong, and the total gross profit for each product is shown in Figure 6.7.
- The first step is to estimate total overheads to be incurred by the business.
- A large organization uses multiple predetermined overhead recovery rates to allocate its expenses to the cost centers.
For some companies, the difference will be very minute or there will be no difference at all between different basis while for some other companies the differences will be significant. Therefore, a company should choose the basis for its predetermined overhead rates carefully after considering all the factors. Various activity and cost bases can be used, including direct labor hours, machine hours, and production units.

Traditional Costing method
Calculating predetermined overhead rates involves estimating total overhead costs and selecting an appropriate allocation base. Now that you’ve calculated your predetermined overhead rate, you can apply it to jobs for the purpose of job costing as the applied overhead cost. Similarly, the predetermined overhead rate allows a business to use consistent costing standards with its products. For example, if a company incurs cooling expenses, then assets = liabilities + equity the expenses are likely to be higher in summer than in winter. This means that if an actual overhead rate is used by the business, the costs of products manufactured in summer will be higher than cost of goods manufactured in the winter. To tackle this problem predetermined overhead rates are used instead of actual overhead rates.
Predetermined Overhead Rate (POHR): Formula and Calculation
Different methods are used to apply predetermined overhead rates based on the chosen cost driver. In larger companies, each department in which different production processes take place usually computes its own predetermined overhead rate. For companies that bill customers based on specific jobs, predetermined overhead rates help determine the overhead portion of job costs.

Cost accountants want to be able to estimate and allocate overhead costs like rent, utilities, and property taxes to the production processes that use these expenses indirectly. Since they can’t just arbitrarily calculate these costs, they must use a rate. Using multiple predetermined overhead rates is more complicated and takes more time, but it is generally thought to be more Medical Billing Process accurate than using a single predetermined overhead rate for the entire plant.
- In addition to this, project planning can also be done with the use of an overhead rate.
- Suppose GX company uses direct labor hours to assign manufacturing overhead cost to job orders.
- Some of the overhead related to monitoring a patient’s health status may overlap, but most of the overhead related to diagnosis and treatment differ from each other.
- The overhead rate of cutting department is based on machine hours and that of finishing department on direct labor cost.
- JKL allocates the manufacturing overhead based on the normal and expected number of production machine hours which are 20,000 for the new year.
- This portion of the process is similar to finding the traditional predetermined overhead rate, where the overhead rate is divided by direct labor dollars, direct labor hours, or machine hours.
Formula for Predetermined Overhead Rate
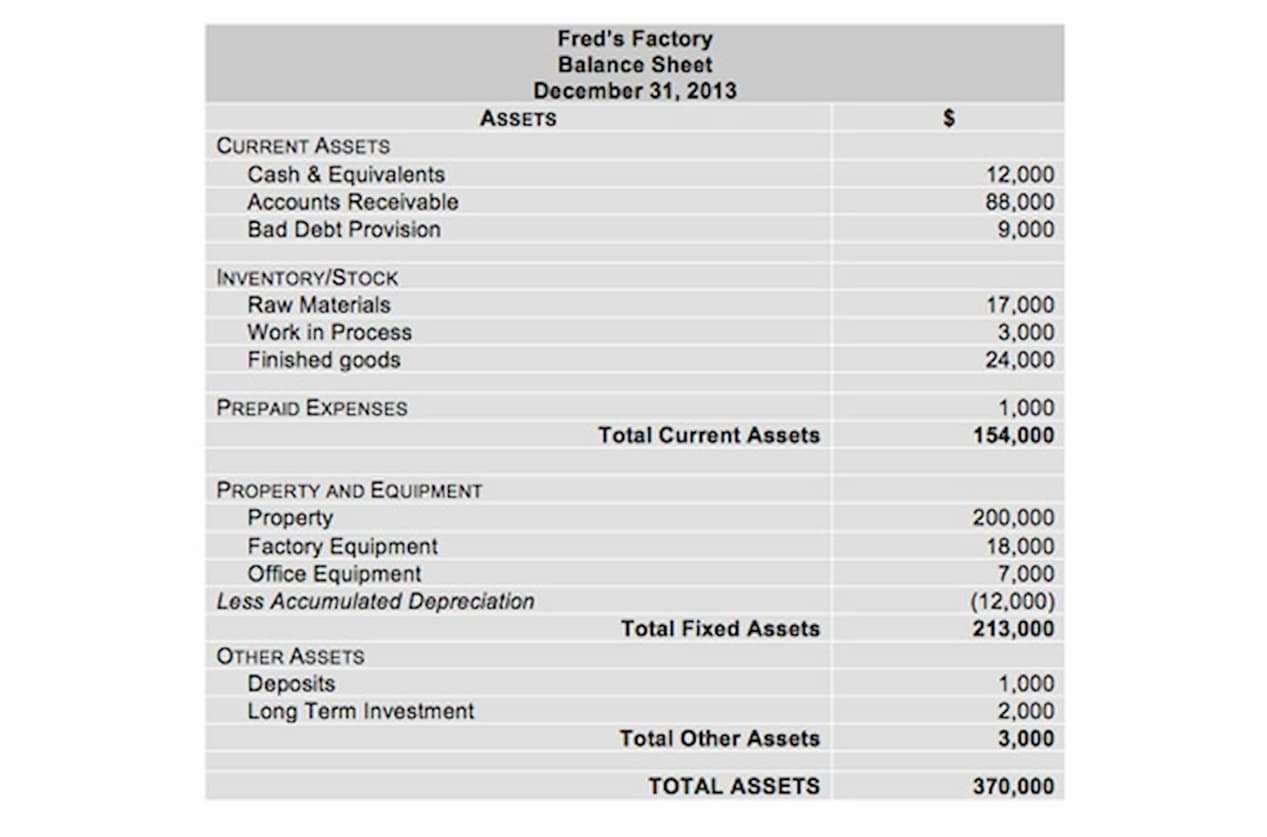
Most companies will adopt the use of predetermined overhead rates in order to know how their products are performing even before the accounting period ends. It is a way to constantly evaluate the profitability of manufacturing instead of waiting until that reporting period comes to an end. The Plantwide overhead rate is the overhead rate that companies use to allocate their entire manufacturing overhead costs to their line of products and other cost objects. This overhead allocation method finds its place in very small entities with a minimized or simple cost structure.
- Commonly, the manufacturing overhead cost for machine hours can be ascertained from the predetermined overhead rate in the manufacturing industry.
- For example, if you use direct labor hours but most of your overhead costs relate to running machines, you’ll miscalculate.
- Therefore, this predetermined overhead rate of 250 is used in the pricing of the new product.
- Therefore, at the end of the period, there might be an underapplied or overapplied overhead, which must be adjusted.
- Cut unnecessary spending – Review budgets to identify and eliminate expenses that do not contribute real business value.
- The fact is production has not taken place and is completely based on previous accounting records or forecasts.
In more complicated cases, a combination of several cost drivers may be used to approximate overhead costs. A number of possible allocation bases are available for predetermined overhead rate the denominator, such as direct labor hours, direct labor dollars, and machine hours. Predetermined overhead is an estimated rate used by the business to absorb overheads in the product cost, and it’s calculated by dividing overheads by the budgeted level of activity.

On the other hand, the machine hours were used to absorb overheads in a machine incentive environment. Yes, it’s a good idea to have predetermined overhead rates for each area of your business. Now, let’s look at some hypothetical business models to see actual use-cases for predetermined overhead rates. The estimated manufacturing overhead cost applied to the job during the accounting period will be 1,450. The estimated manufacturing overhead cost applied to the job during the accounting period will be 1,600. The estimated manufacturing overhead cost applied to the job during the accounting period will be 1,494.
